What is Allergic Contact Dermatitis?
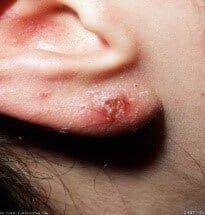
Allergic Contact Dermatitis (ACD) is a red, itchy rash that occurs when the skin, which has become sensitized to a certain substance, encounters that substance again. This is a delayed skin reaction that typically develops 12 – 72 hours after exposure. Some people do not react to allergens at all. Some people will react to an allergen which they had previously tolerated for many years. Skin can become allergic to a substance after many exposures or after just one exposure. For example, most people will have an allergic reaction to poison ivy after just one exposure. Common sources of Allergic Contact Dermatitis include:
- metals, such as nickel (found in jewelry, snaps on jeans, belt buckles, etc.)
- fragrances, for example, those found in perfumes, soaps, lotions, and shampoos
- cosmetics
- topical medications
- preservatives
- sunscreens
- rubber ingredients, which is a common source of work-related allergic contact dermatitis
What are the Symptoms of Allergic Contact Dermatitis?

- reddening of skin (either in patches or all over the body)
- intermittent dry, scaly patches of skin
- blisters that ooze
- burning or itching
- swelling of the skin
- hives
- sun sensitivity
- darkened, “leathery”, and cracked skin
How is Allergic Contact Dermatitis Diagnosed?
If your allergist suspects that you may have a contact dermatitis, patch testing may be recommended. Patch testing differs from other allergy skin testing. No needles or scratches are involved in patch testing. Patch tests involve the placement of various substances/chemicals on the skin (usually on the back if it is rash-free) and are left in place for 48 hours. The patches are held in place with adhesive tape. A thorough patient history will help your allergist determine what substances to use. Usually, the patient is asked to bring in their own personal products, such as cosmetics, shampoos, lotions, soaps, etc. to apply as patch tests. The patches are removed 48 hours after application, and your allergist will interpret the results. Patients are also asked to come back again for a second reading 48 hours after the patch tests were removed for a final reading. At that time, comprehensive teaching/counseling regarding any positive reactions will take place. Patch testing is the only testing available to diagnose ACD.
Our Patch Test Clinic
If you have a skin rash that won’t go away, talk with your allergist. Here at Allergy & Clinical Immunology Associates, we offer patch testing designed to identify and eliminate potential triggers of Allergic Contact Dermatitis. Our patch test clinics include obtaining a detailed patient history, patch test application, reading and interpretation of the results, as well as in-depth patient counseling and management tools. We provide both daytime and evening hours for our clinics to accommodate our patients. Ask your allergist if this service is appropriate for you!